Care Certificate (Part 6) - Communication



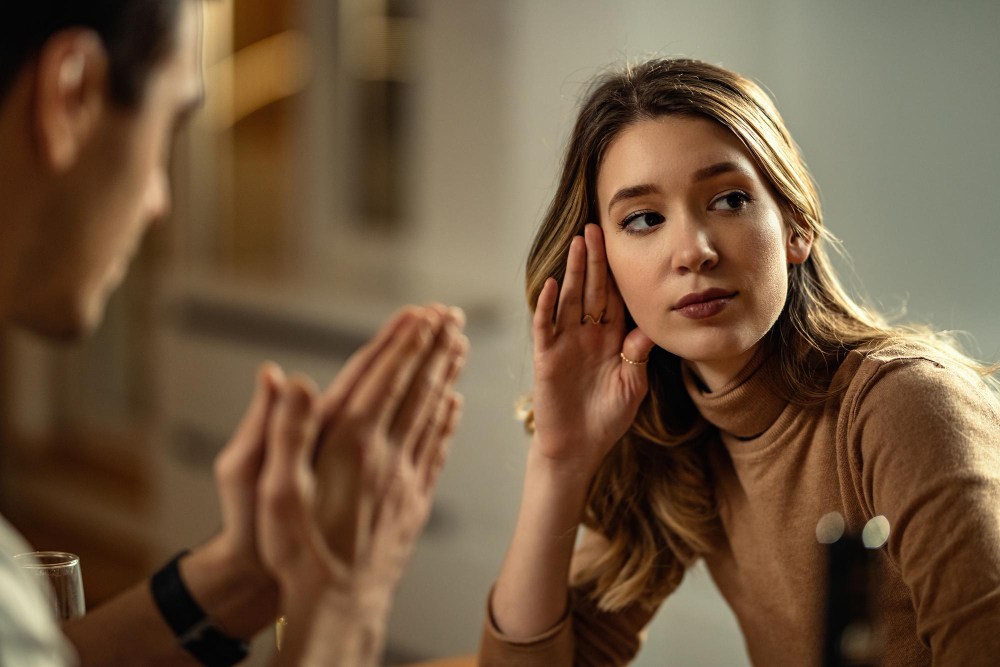
This chapter focuses on the importance of effective communication in health and social care settings. It explores various types of communication, including verbal, non-verbal, written, and alternative methods such as sign language, Makaton, and Braille. Emphasis is placed on recognizing and interpreting non-verbal cues, adapting communication styles to meet individual needs, and understanding the impact of body language, gestures, and facial expressions. The chapter also addresses the significance of formal and informal communication, the importance of understanding an individual's communication needs, and the thoughtful use of touch and physical contact. By mastering these communication skills, care workers can build trusting relationships and provide person-centred care that respects the unique preferences and needs of each individual.
Discover the best online learning for you